The molecular weighs of water is 18.015 and 1L of pure water at 250C weighs about 1000g. Therefore, the molar concentration of water is 1000/18.015 = 55.509 mol L-1. One molecule of water in every 107 molecule dissociate into H+ and OH- ions. However, this slight dissociation of water is very essential for many of chemical processes and reactions in water.
H2O = H+ + OH-
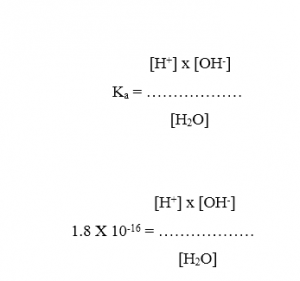
The dissociation constant, Ka, of water at 250C is 1.8 x 10-16 .
Since concentration of H2O is 55.509 M and [H+] is negligible,
so, [H2O] - [H+] → H2O
[H+] x [OH-] = 1.8 x 10-16 x [H2O]
[H+] x [OH-] = 1.8 x 10-16 x 55.509
[H+] x [OH-] = 9.99162 x 10-15
Ion product of water, Kw, is given by,
Kw = [H+] x [OH-] (2)
Kw = 9.99162 x 10-15 (3)
Since, concentration of H+ and OH- in water are equal, therefore, equation (3) can be written as,
Kw = [H+] x [OH-] = [H+]2 (4)
From equation (3) and (4), we can get,
[H+]2 = 9.99162 x 10-15 = 10-14 (5)
Taking negative log on both the sides, equation (5), becomes,
2pH = 14.0
pH = 7.0
The pH of pure water is 7.0 under control conditions, but under ordinary laboratory conditions, pH of distilled water is acidic (pH ≈ 5.0) because of removal of basic cations during distillation and absorption of CO2 from atmosphere.
Remember that a meq of any cation is that amount of cation required to replace 1 meq of another cation.




No Comments